Surging gold stocks lift mining’s top 50 companies above tariff chaos
Posted Under Commodity News, On 21-04-2025
Source: mining.com
World’s 50 most valuable miners are now worth $1.4 trillion, up $80 billion from end-2024 boosted by gold stocks after copper, lithium producers sold off again.
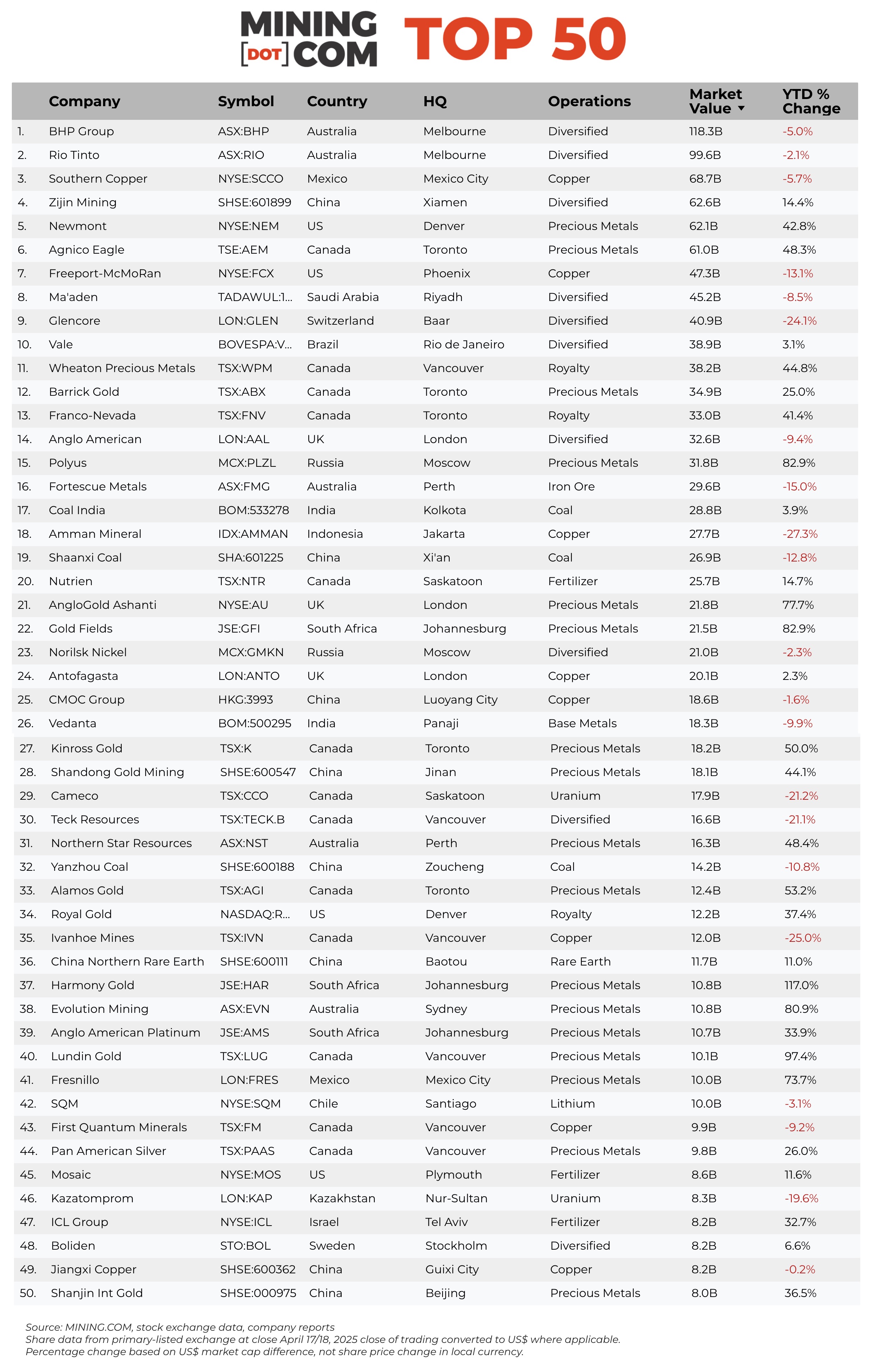
Two weeks into the second quarter, the MINING.COM TOP 50* ranking of the world’s most valuable miners had a combined market capitalization of $1.36 trillion, up $79.7 billion so far in 2025.
The total stock market valuation of the world’s biggest mining companies remains almost $400 billion below the peak hit in the second quarter of 2022.
This snapshot was taken at the close of trading on April 17 and not at the start of Q2 as usual to avoid some of the market distortions brought on by the chaotic weeks following Trump’s on-again off-again tariffs.
This flatters the index to some extent as gold stocks rode the coattails of the record setting bullion price and almost all big names regained some ground after the severe sell-off during the first week of April.
Newcomers
The volatile trading saw the greatest number of new entries – six in all – in a quarter since MINING.COM started tracking the Top 50 six years ago. From $6.7 billion at the end of 2024, the lowest ranked entry must now be worth $8 billion.
Mining and metals arguably suffered some of the biggest swings and roundabouts as the economic effects of a trade war and the focus on critical minerals played havoc – exemplified by the volatility on copper markets.
The bellwether metal hit a record high in the US at the end of March, only to plunge more than 20% over the next week and a half and then make up a big chunk of those losses going into the long weekend.
Amid the hectic trading, copper producers and diversified companies with large base metal portfolios lost a combined $53 billion to April 17 and are now trading $205 billion below their collective peak end-Sep 2024 as the sector’s ranks thin.
Lundin Mining dropped out of the Top 50 during Q1 following another copper counter, Poland’s KGHM, which did not make the cut off in Q4 last year. Q1 was a mixed blessing for the Canadian mining empire with the copper producer making way for Lundin Gold, entering the Top 50 for the first time after doubling in value in USD terms to $10.1 billion in Toronto.
Huayou Cobalt’s inclusion proved to be short-lived while South32 failed to make the cut for the first time since being spun out of BHP a decade ago. The base metals sans copper producer sits at position 51 after being narrowly edged out by Shanjin International Gold, so the stock may well return if (and not necessarily when) profit-taking in gold and gold stocks starts to make sense.
Another notable mover of 2025 is Amman Mineral, the worst performer in the index which lost over $10 billion in value as reality about its piercing run since its debut in Jakarta early 2023 continues to set in. The Indonesian copper-gold company is now worth an eye-catching $20 billion less than its high point at the end of Q2 last year, even after investors ran up the stock more than 20% just in the last week.
Nothing counters gold
While the direction of the copper price over the last few months was almost impossible to judge, gold’s record breaking run looked inevitable. At $3,420 per ounce gold at the time of writing, the yellow metal has now finally also surpassed its 1980 peak in inflation-adjusted terms.
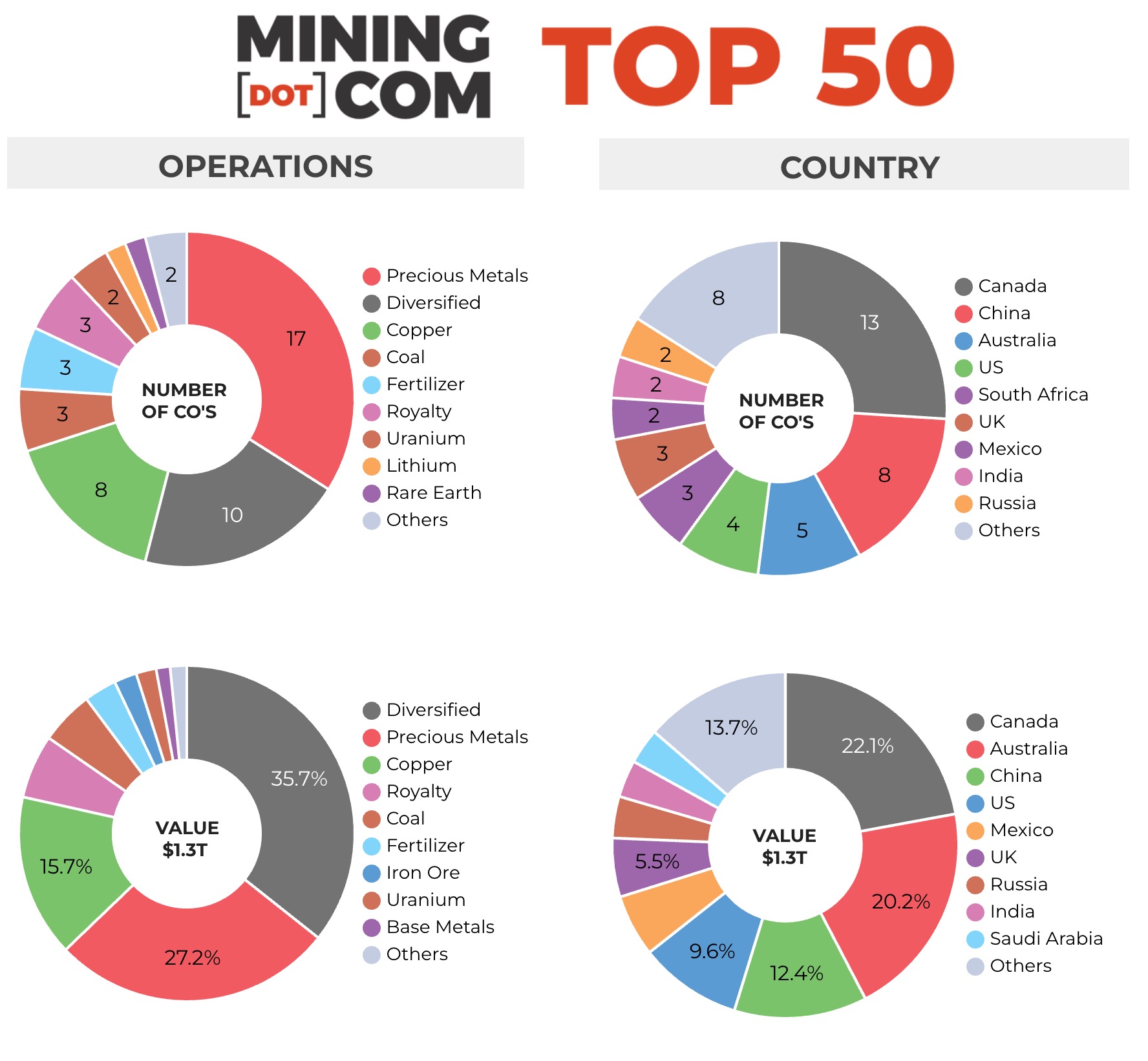
Unsurprisingly, precious metals counters dominate the best performer list and make up the majority of new entrants. Gold, silver and PGM miners and royalty companies now represent a third of the value of the Top 50. The strength in precious metals has also seen Canada overtake Australia for the first time in terms of the value of miners headquartered there.
At 22% of the index, the 13 Canadian companies collectively are worth a smidgen under $300 billion compared to $275 billion for the now eight Australian firms with the inclusion for the first time of Sydney-based gold stock Evolution Mining. In their current form Melbourne-based BHP and Rio Tinto have been the top two global mining stocks since the turn of the century, together worth $220 billion today.
The MINING.COM Top 50 tracks stock value in USD terms not share price gains on local exchange and many stocks in the ranking benefitted from strengthening currencies against the USD.
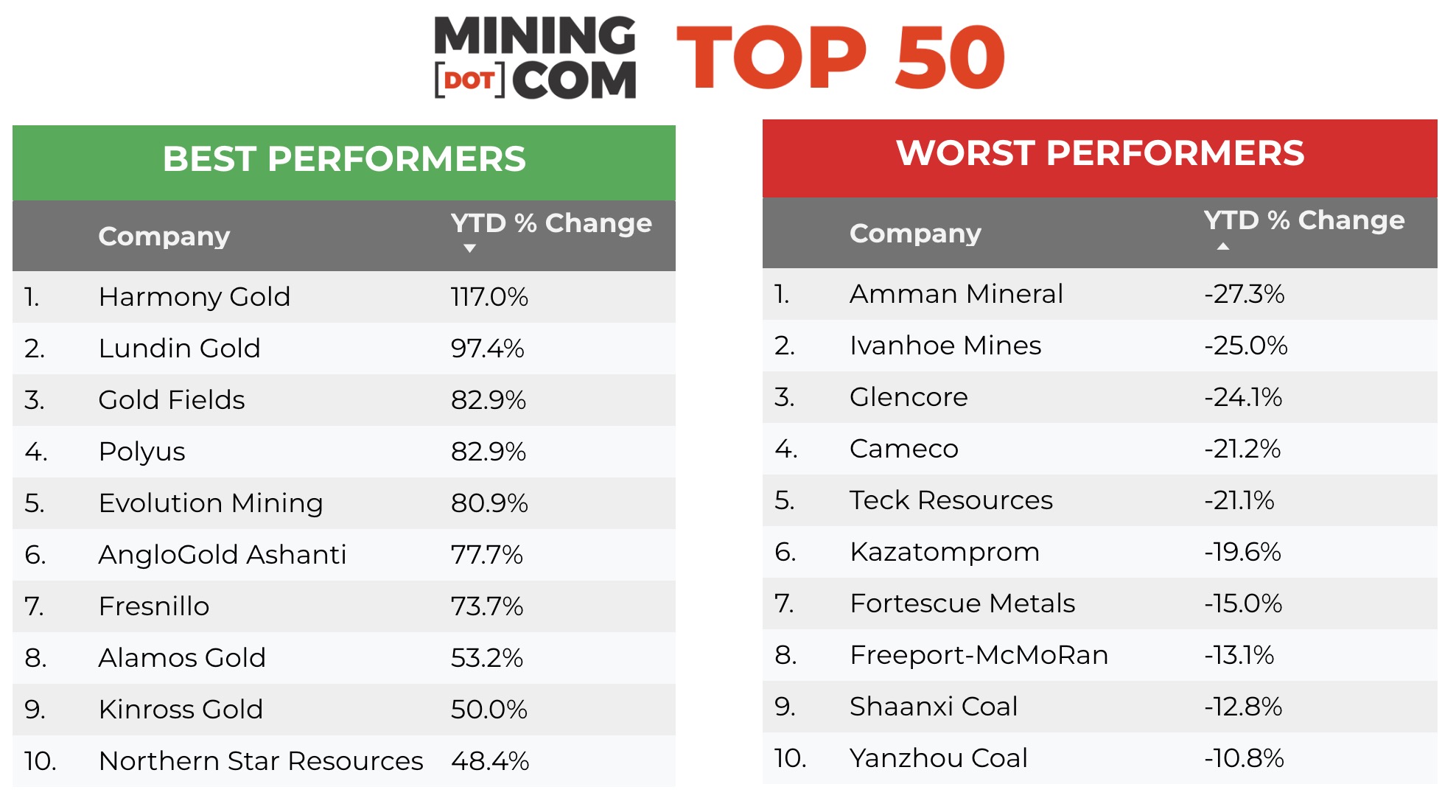
South Africa’s Harmony Gold tops the gainers after jumping 24 spots to enter the ranking at no 37 following a 117% advance since end-2024. Like Harmony, Goldfields also benefited from the strong rand against the greenback, lifting the Johannesburg-based company’s shares by 83% year to date.
Russia’s Polyus, which added $14.4 billion in Q1, was only beaten by the top two gold stocks Newmont and Agnico Eagle which added $18.6 billion and $19.9 billion year to date in market cap gains. The ruble has strengthened by 20% against the US dollar in 2025 and Norilsk Nickel, thanks to captive investors on the MCX, has maintained its good standing in the Top 50 despite sanctions and trading restrictions. Norilsk is still worth north of $20 billion but still a far cry from its peak position as the world’s number 5 most valuable mining company reached mid-2021.
London-listed Fresnillo returns to the index after years in the wilderness thanks to a 74% surge in value for the Mexican silver and gold miner, majority owned by Mexican industrial group Peñoles. Together with Southern Copper, owned by Grupo Mexico, the country now represents nearly 6% of the value of the Top 50.
Gold counters are likely to only increase in number and size over the rest of 2025. Kazatomprom dual-listed in London and Astana in 2018, and Uzbekistan is now readying an IPO for Navoi Mining and Metallurgy Combinat – the world’s fourth largest gold mining company and significant uranium producer later this year.
Rare earth representation
China Northern Rare Earth is the only producer of the 17 elements in the ranking and despite the frenzy surrounding the sector as China tightens control. There are no obvious REE candidates that could join the Top 50 in short order.
MP Materials, which operates the Mountain Pass mine in California, has surged by 69% in value year to date but the Las Vegas-based company is still worth only $4.3 billion.
The company’s valuation peaked above $8 billion in March 2022, but the whole mining industry was riding high at the time and the high price ticket for entry at the time meant it fell just outside the ranking. Australia’s Lynas Rare Earths have also come close in the past and is up 26% this year for a valuation of $5.3 billion.
Lithium down to a single stock
Lithium’s representation in the ranking is down from six companies to a single stock – Chile’s SQM languishing in position 42 and worth less than $10 billion – following the exit of China’s Tianqi and US-based Albemarle during the quarter, with the latter dropping by 38% in 2025.
The value destruction caused by the slump in lithium prices has been nothing short of astonishing. Lithium stocks in the index peaked in the second quarter of 2022 with a combined value of nearly $120 billion.
While Albemarle now worth $6.2 billion may well make a comeback (the longer term prospects for lithium demand remains bright), the absorption of Arcadium by Rio Tinto makes it unlikely that the Top 50 will see a rush of lithium stocks any time soon, a rebound of the commodity notwithstanding.
Zangge Mining, which does derive a good proportion of income from lithium, but is mostly a fertilizer producer, is bubbling under at number 53. The Chinese company may not stick around either – it’s the subject of takeover overtures by Zijing Mining, which also helps explain the 25% rise in the stock on the Shenzen exchange in USD terms.
Notes:
Source: MINING.COM, stock exchange data, company reports. Share data from primary-listed exchange at close April 17/18, 2025 close of trading converted to US$ where applicable. Percentage change based on US$ market cap difference, not share price change in local currency.
As with any ranking, criteria for inclusion are contentious. We decided to exclude unlisted and state-owned enterprises at the outset due to a lack of information. That, of course, excludes giants like Chile’s Codelco, Uzbekistan’s Navoi Mining (the gold and uranium giant may list later this year), Eurochem, a major potash firm, and a number of entities in China and developing countries around the world.
Another central criterion was the depth of involvement in the industry, and how far upstream is the bulk of its revenue, before an enterprise can rightfully be called a mining company.
For instance, should smelter companies or commodity traders that own minority stakes in mining assets be included, especially if these investments have no operational component or even warrant a seat on the board?
This is a common structure in Asia and excluding these types of companies removed well-known names like Japan’s Marubeni and Mitsui, Korea Zinc and Chile’s Copec.
Levels of operational or strategic involvement and size of shareholding were other central considerations. Do streaming and royalty companies that receive metals from mining operations without shareholding qualify or are they just specialized financing vehicles? We included Franco Nevada, Royal Gold and Wheaton Precious Metals on the basis of their deep involvement in the industry.
Vertically integrated concerns like Alcoa and energy companies such as Shenhua Energy or Bayan Resources where power, ports and railways make up a large portion of revenues pose a problem. The revenue mix also tends to change alongside volatile coal prices. Same goes for battery makers like China’s CATL which is increasingly moving upstream, but where mining will continue to represent a small portion of its valuation.
Another consideration is diversified companies such as Anglo American with separately listed majority-owned subsidiaries. We’ve included Angloplat in the ranking but excluded Kumba Iron Ore in which Anglo has a 70% stake to avoid double counting. Similarly we excluded Hindustan Zinc which is listed separately but majority owned by Vedanta.
With other groups like Mexico’s Penoles where refining and chemicals make up a substantial part of the business where possible the Top 50 would include separately listed operating subsidiaries that are dedicated to mining. This is also why Southern Copper represents Grupo Mexico in the ranking.
Many steelmakers own and often operate iron ore and other metal mines, but in the interest of balance and diversity we excluded the steel industry, and with that many companies that have substantial mining assets including giants like ArcelorMittal, Magnitogorsk, Ternium, Baosteel and many others.
Head office refers to operational headquarters wherever applicable, for example BHP and Rio Tinto are shown as Melbourne, Australia, but Antofagasta is the exception that proves the rule. We consider the company’s HQ to be in London, where it has been listed since the late 1800s.
Please let us know of any errors, omissions, deletions or additions to the ranking or suggest a different methodology: email Frik Els at fels@mining.com with Top 50 in the subject line.

